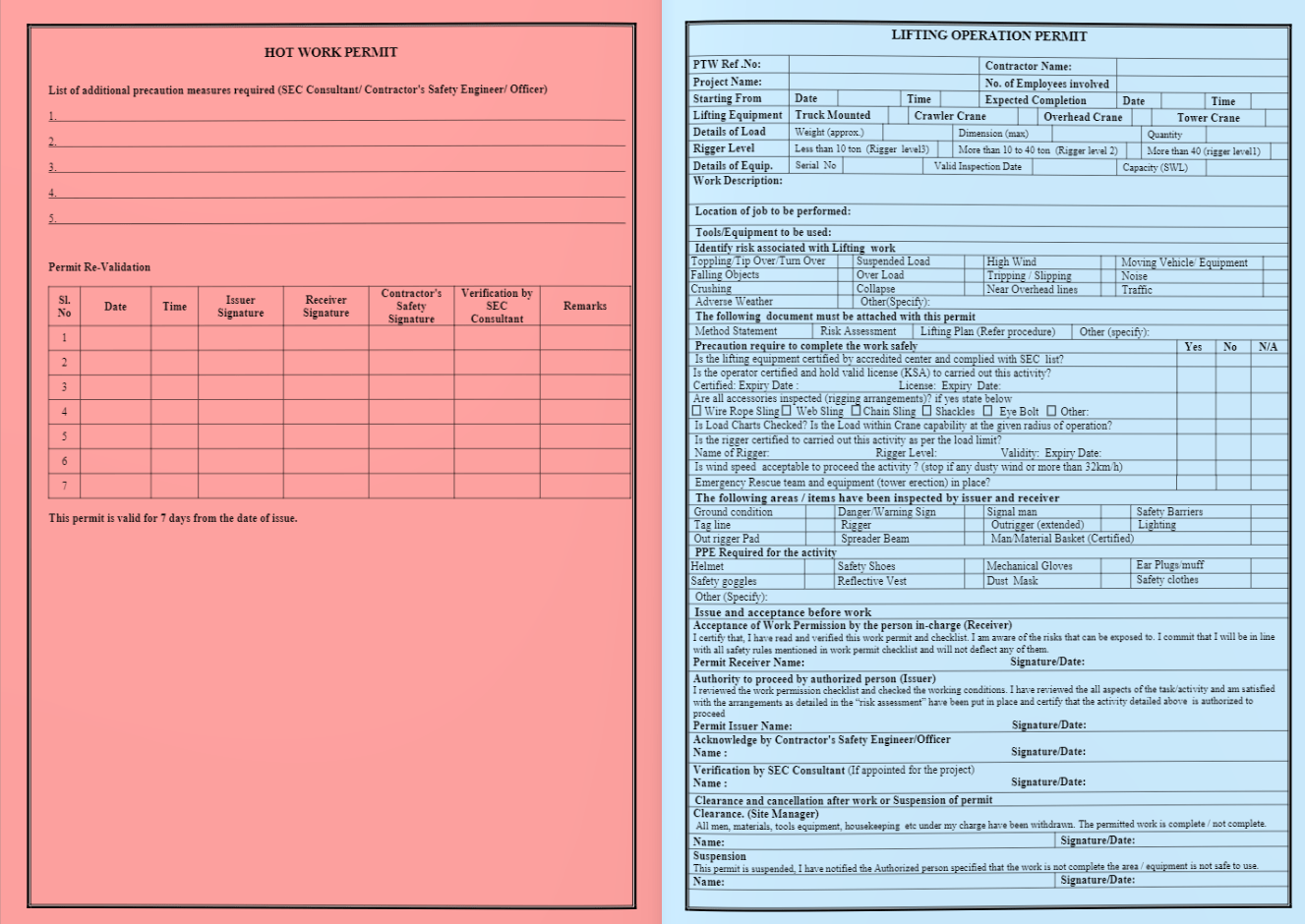
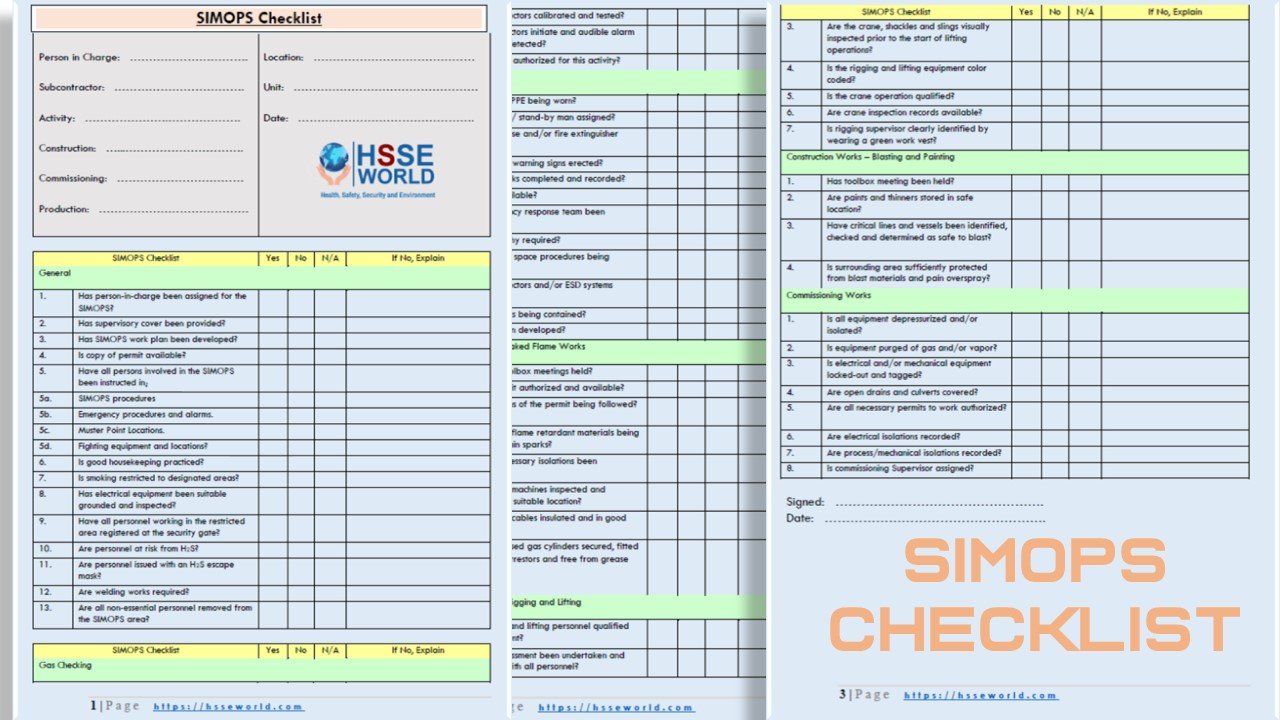
Permits to work play an important part in safe systems of work for many maintenance activities. Laid out below is an in-depth look at everything you need to know about Permits to Work and how they contribute to making high-risk tasks safer. Keeping in track with all the requirements can be very time consuming, so using a permit to work Forms has proven value across numerous organizations so
What is the definition of a Permit to Work in Health and Safety?
Permit to Work (PTW) is a documented management system to ensure work is done safely and efficiently. Mostly used in hazardous industries but also used for known hazardous tasks across all industries.
Read the the Permit to work 7 forms by Flipping book :
Why would you need a Permit to Work the System?
Permit to work involves procedures that authorize certain people to carry out specific work within a specified time frame. It sets out the precautions required to complete the work safely, based on a hse risk assessment, and is, therefore, a core element of safe systems of work.
The ‘permit-to-work form’, is a written and signed statement resulting from the work safety procedure, ensuring both the establishment of safe conditions for the work to commence and the maintenance of safe conditions for the duration of the work, including the provision of emergency arrangements. An agreed safe system of work for the job task, which prevents instructions from being missed and/or misinterpretation of instructions.
They can also serve as a checklist and a training document to ensure that all hazards, protective measures, work instructions, and general requirements have been reviewed and understood by the assigned workers.
What is a permit to work used for?
A permit to work is used to identify the work to be completed in the following areas:
- What will be done and how it will be done(method statement/work procedure)
- The hazards involved
- The preparation necessary
- The precautions or protective measures to be taken
- The work procedures
- Authorize certain people to carry out specific work within a specified timeframe
- Declarations from the people authorizing the work, carrying out the work, and all involved in the work task/project
- A declaration from the permit originator that work has been completed or the equipment/machinery etc. being worked on is ready for normal use
They are the result of collaboration with all who will be involved in the work to ensure that authorized and competent people have thought about foreseeable risks and that such risks are avoided by using suitable precautions. The issue of a permit does not, by itself, make a job safe. Other precautions may need to be taken – e.g. electrical isolation, and access barriers. Those who are trained and responsible must follow the instructions correctly.
Why is a Permit to Work deemed important?
The purpose is to make high-risk job tasks in the workplace safer to conduct. For example, construction work such as hot works, excavation, confined space work, etc. requires work permits. To prevent incidents, it is vital that there be effective management of hazards including safe systems of work and permit-to-work systems are a vital part of effective management of the hazards and are an integral part of a safe system of work. The aim of the permit to work system is to ensure that the task is carried out in accordance with the carefully considered conditions specified in a permit drawn up and independently verified by competent individuals.
What issues may contribute to a major accident or hazard?
- Failing of the site safety management system
- Failure to recognize a hazard before and during the job task
- Failure to comply with the work permit system in hazardous environments
- Communication failure during the use of a work permit system
A permit to work system is often used for hazardous job types such as confined space work, hot work etc. These jobs require employees to enter and work in confined spaces, to repair, maintain, or inspect electrical installations, or to use large or complex equipment.
What is the duration of a Permit to Work?
The duration of the work permit is not specified and is unique to the job task or the project in hand. The duration will be agreed upon by those involved in the preparation of the permit and the permit method statement. Most often hot work permits are limited to 30 days, but this is only a guideline.
Permits to work are required whenever there is a significant risk to safety and health during an operation, and where precise preparation of the site or plant and clear communications of procedures is needed to control the risk.
Who can issue a Permit to Work?
Permits should be issued, checked, and signed off by someone who is competent to do so, and who is not involved in undertaking the work.
.png?width=758&name=Screenshot%20(62).png)
What is a Permit to Work procedure method?
A permit to work procedure is a means of achieving effective control of a system of work through formal written documentation known as a permit to work form. The essential components of a permit-to-work system include:
- A written procedure (Safety Procedure/Work Instruction), setting out how the system/job is to operate and clearly defining who may authorize jobs and who is responsible for specifying and implementing the necessary precautions
- Permit-to-work form
- A method of informing the persons carrying out the work of the exact identity, location, nature, and extent of the job, the hazards involved and the precautions to be taken, and
- A system for ensuring the safe hand-back of the workplace after the job is completed and, in the case of confined space entry, after the space is vacated (HSA, 2020).
The safety procedure must:
1. Clearly identify the kinds of jobs requiring work permits
2. Explain how the permit system works, for example:
- When to apply for a permit (how many hours before the work is started?)
- Where to get a permit?
- How to fill it out?
- How many copies are needed?
- Who gets copies?
- Who must be informed of the work?
- What to do with the permit when work is stopped or completed?
3. Define responsibilities, for example:
- Who fills out the form?
- Who identifies hazards?
- Who ensures precautions have been taken?
- Who issues/revokes permits?
- Who supervises the work?
- Who ensures work is completed (must be authorized and agreed upon before job task is commenced)?
Also Read: 35 Inspection forms for Rig Check
Permit to Work Hazards
A work permit should be used when there is danger from any of the following hazards:
- Fire
- Sparks from open flames, welding, cutting, furnaces, etc.
- Explosive, corrosive, or toxic gases or atmospheres
- Pressure systems
- Steam or other hot materials (burns)
- Electricity and other energy sources
- Accidental start-up of mechanical equipment
- Oxygen deficiency or oxygen enrichment
- Suffocation or drowning (for example, in bulk material bins or solvent storage tanks)
- Restricted access, exit, and movement
- Toxic substances
- Radioactive materials
- Lasers
- Temperature extremes
- Any other recognized serious safety or health hazard
What are the different types of Permit to Work?
The different types of permits include:
Hot Work Permits – issued for work using or generating heat that is sufficient to ignite gases, vapors, dust, etc. Some examples are welding, flame-cutting, and metal drilling.
Safety Permits – issued when work involves steam, water, air, or electricity. Safety permits are also needed when repair or maintenance work requires locking out of energy sources.
Entry Permits – used when workers are required to enter and work in confined spaces such as silos (manufacturing of cereals), tanks, or pits. This type of permit is often combined with the other permits listed here, depending upon the nature of the work to be carried out in the confined space.
Unique Permits – issued when work involves hazardous conditions such as working near radioactive materials, working at heights, or carrying out other specialized work.
General Permits – issued for highly hazardous jobs of a more general nature that are not covered by any of the permits described above.
Permit to Work Guidelines
In order for the permit to work to achieve its aims and fulfill its purpose, it needs to cover all the legal requirements and essential points, control the risk sufficiently, and clearly set out the procedures in place.
- Display at the job site
- A copy is to be kept with the issuing authority
- Communicate your Policy and Work Procedures
- Provide Training
- General Information to Include in Your Work Permit:
- Permit title
- Permit reference number
- Job Location
- Plant Identification
- Description of work to be done and its limitations
- Hazard identification
- Precautions necessary and action in the event of an emergency – people who carried out precautions.
- Protective equipment
- Issue – signature (issuing authority) confirming that precautions have been taken and any isolations have been made. Date, time, and duration of the permit.
- Acceptance – signature(S) confirming understanding of work to be done, hazards involved, and precautions required. Also confirming that permit information has been explained to all permit users.
- Extension/shift handover procedures – signatures confirming checks made that plant remains safe to be worked on and new authorities and permit users are made fully aware of the hazards and the precautions. A new expiry time is given.
- Hand back – signed by performing authority to certify that the work is completed. Signed by issuing authority to certify the work is completed and the plant is ready for testing and recommissioning.
- Cancellation – certifying work tested and plant successfully recommissioned.
Also, Read Hazard Identification Plan (HIP) Template
Download The Forms
Permit To work Forms
More Downloads
- Welding, Cutting, and Brazing Checklist
- Construction Safety Inspection Checklist
- Permit To work Forms
- Hazard Identification Plan (HIP) Template
- Pre-Startup Safety Review Checklist (PSSR)
- 35 Inspection forms for Rig Check
- Chemical Risk Assessment form
- 22-Safety Inspection Checklists
- Safety Task Assessment Form
- Suspended Scaffold Pre-Operation Inspection Checklist
- Grating-Decking-Floor- handrail-Removal Form
- Electrical Inspection Checklists
- Annual Internal Audit Form
- Mobile Scaffold Inspection checklist
- Simultaneous Operation (SIMOPS) checklist
- Temporary Construction Facilities (TCF) Inspection checklist
- HIRA, HSE Hazards & Effects Management Process (HEMP) & Risk Register Template
- Ladder Inspection Form
- Construction safety Inspection checklist
- Equipment Safe Operating Procedures- SOP 61 checklist
- Permit to Work (PTW ) AUDIT CHECKLIST
- Hygiene and Sanitation Inspection Checklist
- Electric Arc Welding and Cutting Checklist
- Pressure Testing Checklist
- Crane Suspended Personnel Platform (MANBASKET) Permit
- Laboratory Inspection Checklist Form
- CRANE INSPECTION REPORT
- Scaffold Register and Inspection Checklist
- Portable Ladder Self Inspection checklist
- Process Safety Management (PSM) Compliance checklist
- OSHA Inspection Checklist 8-Pages
- Job Hazard Analysis form
- Incident Report Form
- Safety Inspection Form
- Contractor Weekly HSE Report Form
- Competent Person Designation form
- Compressed Gas Cylinders Access Control Inspection Checklist
- Emergency Drill After Action Review form
- Emergency Drill Table Top meeting Form
- Slips,Trips and Falls checklist
- Lift Plan Form
- Machines Access Control Inspection Checklists
- Camp Inspection form