SELF-INSPECTION. The most widely accepted way to identify hazards in the workplace is to conduct safety and health self-inspections. You can only be certain that actual situations exist in the workplace if you check them from time to time.
Begin a program of self-inspection in your workplace. Self-inspection is necessary if you are to know where probable hazards exist and whether they are under control.
This Article contains twenty-two safety inspection checklists designed to help you evaluate your work areas. They will give you some indication of where you should begin action to make your workplace safer and more healthful for your employees.

These checklists are not all-inclusive. You may wish to add to them or delete portions that do not apply to your workplace. Carefully consider each item as you come to it and then make your decision. Do not spend time with items that have no application to your workplace. Make sure you check each item on the list and leave nothing to memory or chance. Write down what you see (or do not see) and what you think should be done about it. YOU MUST COMPLY WITH THE OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY AND HEALTH LAW FOR MANY OF THE TOPICS COVERED IN THESE CHECKLISTS.
When you have completed the checklists, you will have enough information to decide if problems exist. Once you have identified hazards, you can begin corrective actions and control procedures.
SCOPE. The scope of self-inspections should cover the following areas:
- Processing, Receiving, Shipping and Storage. Equipment, job planning, layout, heights, floor loads, materials handling, and storage methods.
- Building and Grounds. Floors, walls, ceilings, exits, stairs, walkways, ramps, platforms, driveways, and aisles.
- Housekeeping Program. Waste disposal, tools, objects, materials, leakage and spillage, cleaning methods, schedules, work areas, remote areas, and storage areas.
- Electrical. Equipment, switches, breakers, fuses, switch boxes, junctions, special fixtures, circuits, insulation, extension cords, tools, motors, grounding, compliance with codes.
- Lighting. Type, intensity, controls, conditions, diffusion, location, glare, and shadow control.
- Heating and Ventilation. Type, effectiveness, temperature, humidity, controls, natural and artificial ventilation, and exhausting.
- Machinery. Points of operation, flywheels, gears, shafts, pulleys, keyways, belts, couplings, sprockets, chains frames, controls, lighting for tools and equipment, brakes, exhausting, feeding, oiling, adjusting, maintenance, lockout, grounding, workspace, location and purchasing standards.
- Personnel. Training, experience, methods of checking machines before use, clothing, personnel protective equipment, use of guards, tool storage, work practices, method of cleaning, oiling, or adjusting machinery.
- Hand and Power Tools. Purchasing standards, inspection, storage, repair, types, maintenance, grounding, use, and handling.
- Chemicals. Storage, handling, transportation, spills, disposal, amounts used, toxicity or other harmful effects, warning signs, supervision, material safety data sheets, supervision, training, personal protective equipment, and clothing.
- Fire Prevention. Extinguishers, alarms, sprinklers, smoking rules, exits, personnel assignments, separation of flammable materials and dangerous operations, explosive-proof fixtures in hazardous locations, and waste disposal.
- Maintenance. Regularity, effectiveness, training of personnel, materials, and equipment used, records maintained, method of locking out machinery, and general methods.
- Personal Protective Equipment. Type, size, maintenance, repair, storage, assignment of responsibility, purchasing methods, standards observed, training in care and use, rules of use, and method of assignment.
( learn more about workplace-inspections/ )
The attached file below includes the following Inspection checklists:
- General work environment
- Hazard communication program
- Personal protective equipment
- Electrical safety
- Hazardous chemical exposure
- Confined space operations
- Fire safety
- Lockout and Tagout procedures
- Medical services and first aid
- Scaffold safety
- Industrial noise
- Hand and power tools and equipment
- Construction site safety
- Portable ladder safety
- Transporting employees and materials
- Machine guarding safety
- Compressors and compressed gas cylinders
- Motor vehicle service and repair operations
- Welding and hot work operations
- Spray painting operations
- Hoists and auxiliary equipment
- Forklifts and industrial trucks
Snapshot of some checklists
These checklists are not all inclusive. You may wish to add to them or delete portions that do not apply to your workplace. Carefully consider each item as you come to it and then make your decision. Do not spend time with items that have no application to your workplace.
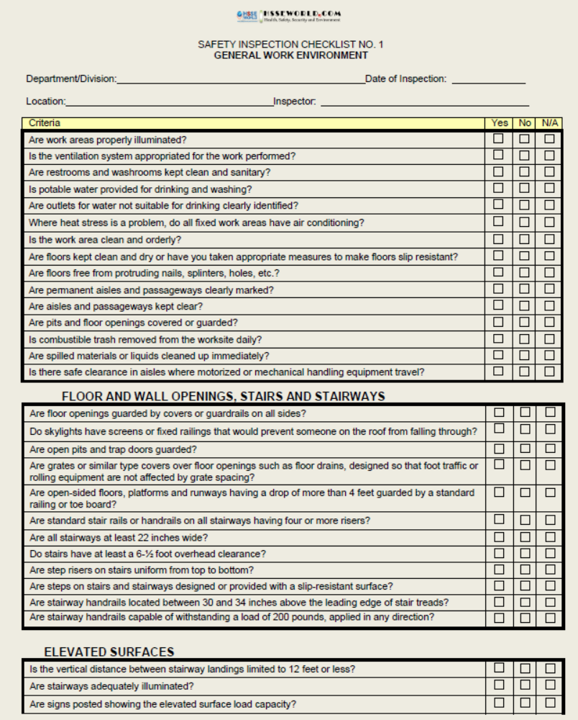

This Document contains twenty-two safety inspection checklists designed to help you evaluate your work areas. They will give you some indication of where you should begin action to make your workplace safer and more healthful for your employees.
Now you can download the PDF and editable Form and use it to fit your purpose just click on download below
Download the Checklists
22-Safety Inspection Checklists PDF
22-Safety Inspection Checklists Doc


