The objective of the Hazard Identification Risk Assessment (HIRA) is to identifying and assessing the hazard associated with the construction of the project and thereby controlling the risk by implementing mitigation measures before the start of the work to avoid the incident. HIRA helps to become proactive rather than just reactive.
The following terms used in HIRA
ALARP: As Low As Reasonably Practicable. This is the level, where the time, effort, difficulty, and cost of further reduction measures becomes disproportionate to the additional risk reduction from the incremental effects.
CONSEQUENCE: The unmitigated impact of the hazard in terms of People, Environment, Asset, and Reputation.
WHAT IS HAZARD?
Hazard is a potential condition awaiting to be converted into an accident if proper precautions are not taken into consideration. Hazard is the mother of the accident.
HIERARCHY OF CONTROLS: Order of preference in the application of risk mitigations. The order is: Eliminate, Substitute, Isolate, Engineer, Administration, and PPE.
PROBABILITY: The possibility of the event happening.
WHAT IS RISK?
The chances of a hazard actually causing an injury or disease. MAJOR RISK: A risk that has the potential to result in a Major Accident classified as high risk to people, assets, the environment, and/or company reputation as defined in TPL SHE Risk Matrix.
The acronyms used in HIRA have the meaning defined below:
| E&I | Electrical and Instrumentation |
| HIRA | Hazard Identification Risk Assessment |
| SHE | Safety, Health, and Environment |
| HRA | Health Risk Assessment |
| RAM | Risk Assessment Matrix |
| OCP | Operational Control Procedure |
| HIRAC | Hazard Identification Risk Assessment and Control |
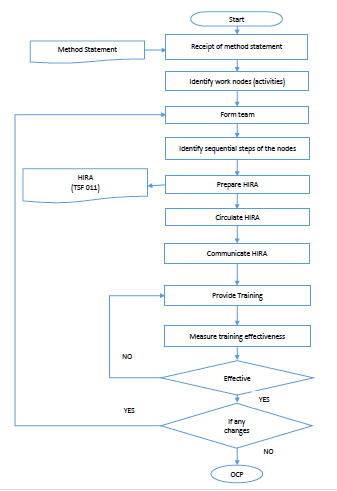
HIRA ORGANISATION STRUCTURE

RESPONSIBILITIES OF HIRA TEAM
| S. No. | Person | Responsibility |
| 1. | RCM/CPM/ PM | 1. RCM is a process owner. 2. To form a HIRA Cross-functional team along with Site In-charge/Engineer (Civil, Electrical, Mechanical), Safety In-charge, Fleet, HR/Admin, and subcontractor representative. 3. Any material to be required as per the Precautionary measures and proposed control measures need to arrange 4. To review the updated HIRA and approve it. |
| 2. | Site In-charge | 1. To prepare the Method statement of each activity. 2. To participate in preparing HIRA. 3. To incorporate all the Hazard & appropriated precautionary measures as per the site environment, to bring down the risk level to the acceptable risk and communicate down the level. 4. Before issuing PTW ensure all precautionary measures are in place. 5. Ensure HIRA talk by site supervisor before starting the activity. |
| 3. | Safety In-charge | 1. Work as Facilitator to prepare HIRA based on the method statement. 2. Ensure all concerned person is available for preparing HIRA. 3. To incorporate all the Hazard & appropriated precautionary measures in HIRA format along with responsibility. 4. Communicate updated HIRA to all concern for implementation and ensure all precautionary measures are in place. The same shall be communicated to SBG SHE Head and Corporate SHE Team. 5. To ensure safety supervisor shall monitor for any deviation. 6. If any deviation, escalate to Site In-charge, RCM/CPM/PM, and SHE Head. |
| 4. | Sub-contractor Representative | Follow the precautionary measure as per the HIRA |
FREQUENCY OF HIRA
- The site Team needs to prepare Dynamic HIRA along with the proposed control measure on the basis of Master HIRA.
- HIRA needs to be prepared before the start of each activity.
- HIRA needs to be updated after the occurrence of any incident, management of change, change of work methodology, and change of any regulation. If there is no change then it should be reviewed half-yearly.
METHODOLOGY OF HIRA
The HIRA review is the structured multidisciplinary hazard identification, risk assessment, and methodology that provides a detailed review of hazard, risk, and control of the construction activities. The review is facilitated by the relevant construction personnel in the brainstorming session.
Overview of HIRA Methodology
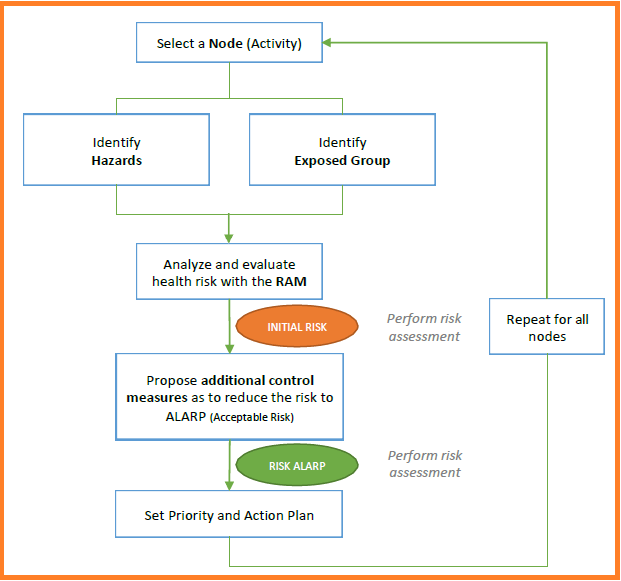
HIRA Flow chart
The steps of HIRA review is summarised as follows:
- Classify work/assessment units or work activities during the construction phase (based on Work Method Statement).
- Identify the hazards associated with work activities.
- List the Consequence of the hazard involved in the activity.
- Assess and score the risk (i.e. probability X severity) using the Risk Matrix as per TPL Risk Assessment Matrix (RAM).
- List out present controls (preventive and recovery).
- Assess the risk based on present controls.
- Reassess the medium and high risk to bring it down to acceptable risk.
- Verify compliance to regional Regulations, Project Specifications, and applicable international codes and standards.
TPL SHE RISK ASSESSMENT MATRIX
For each of the identified hazards, the level of risk is assessed based on the TPL SHE Risk Assessment Matrix during the HIRA review. Risk ranking is firstly performed based on the unmitigated risk for each hazard, and then the level of risk is re-evaluated after taking into consideration of the existing prevention/mitigation measures and controls.
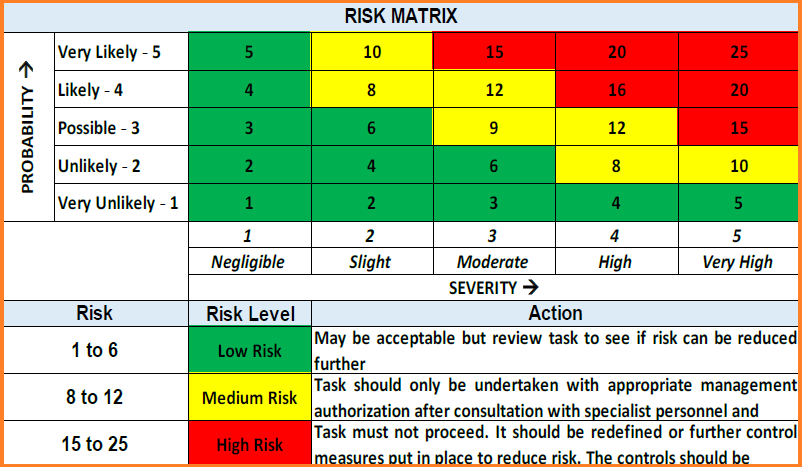
If the risk is in the Green region on the TPL SHE RAM, this is broadly acceptable and no further action is required. If the risk is in the Yellow region on the TPL SHE RAM, this is in the tolerable regions and needs to be demonstrated to be As Low As Reasonably Achievable (ALARP) by recommending further action.
If the Risk is still in the Red region, this is not acceptable and action definitely needs to be taken. HIRA Review team shall discuss the proposed actions, where applicable, to address the hazard that is ascribed with a medium to high-risk rating.
CONTROL MEASURES
Controls are required to be separated into preventive and recovery. Controls are required to be categorized using the hierarchy of controls (eliminate, substitute, isolate, engineering, administrative, and PPE). This allows the review of controls to ensure the principle of inherently safer construction is being applied.

EFFECTIVENESS
- Present Risk reduced to Acceptable Risk
- Reduction of incident
- Reduction in repetitive observation
- Improvement in Behavioural Safety
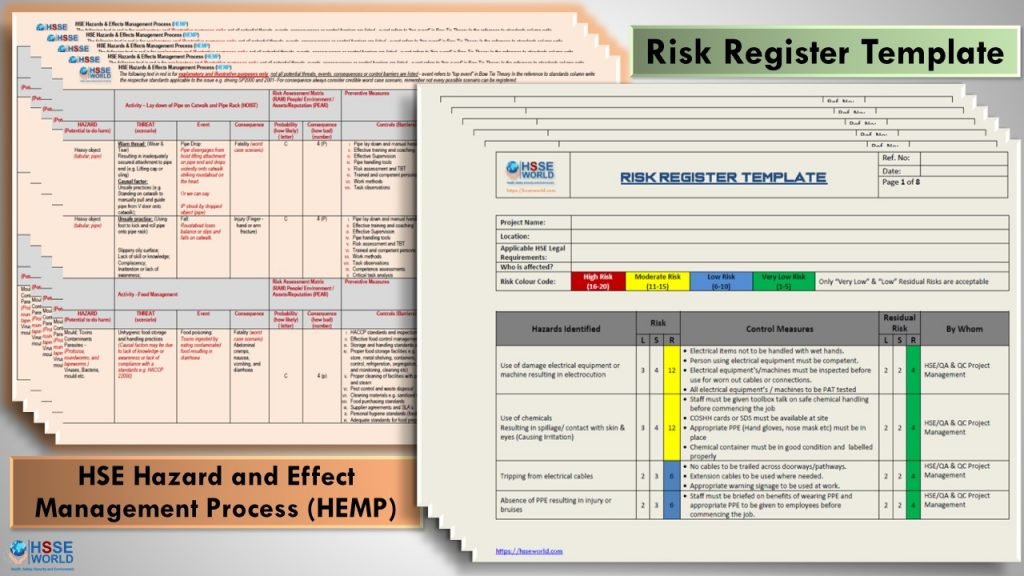
Download The Templates
HSE Hazards & Effects Management Process (HEMP) & Risk Register Template could be used as a guideline during preparing hazard identification and Risk Assessment HIRA the templates are editable and could be modified to fit your purpose
Download Risk Register Template
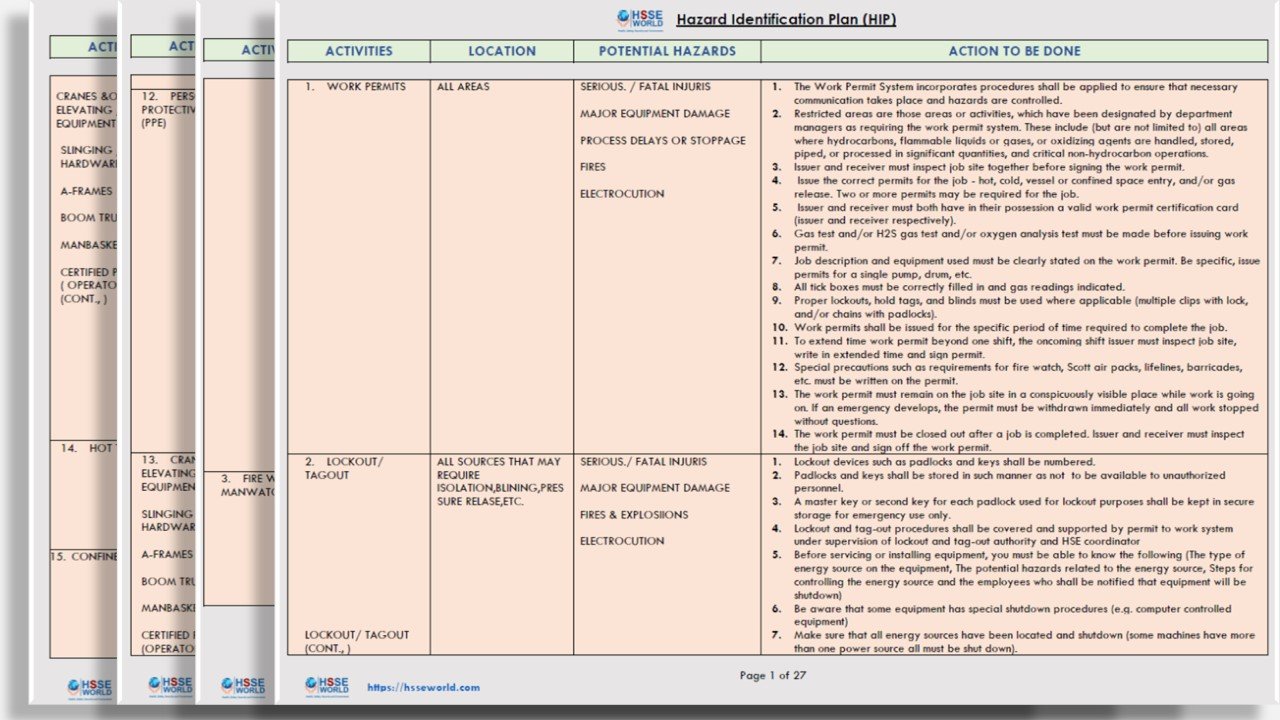
Download HIRA Template
(learn more : hazard-identification-plan-hip-template/)




0 thoughts on “HIRA, HSE Hazards & Effects Management Process (HEMP) & Risk Register Template”